The Windows operating system is a pretty study and adaptable OS but like any other application or software there might be instances where a glitch may occur causing you to lose your work, loose internet connectivity or the PC might crash altogether. Being able to recognize these issues and understanding how to resolve them can help to save you both time and frustration. In this post I’ll guide you through 5 common issues that you might run into while operating a Windows PC and how to troubleshoot them.
1. Slow Performance
Windows machines can experience sluggish and poor performance for a variety of reasons such as too many background programs running, malware, overheating, insufficient disk space, outdated drivers, or even system updates.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Task Manager: Use the key combination “Ctrl + Shift + Esc” to open Task Manager and check your running processes. Identify and terminate any processes consuming excessive CPU, memory, or disk resources.
- Scan for Malware: Use a trusted antivirus or anti-malware tool to detect and remove malicious software.
- Restart the System: A simple restart clears temporary files and resets running processes.
- Free Up Disk Space: Ensure that the primary drive (usually C:) has adequate free space. Use Disk Cleanup or a third-party tool if necessary.
- Update Drivers: Outdated drivers can degrade performance. Use Device Manager or Windows Update to ensure all drivers are up to date.
- Install Pending Updates: Outdated system components can cause slowdowns. Make sure your system is fully updated.
Microsoft Resources:
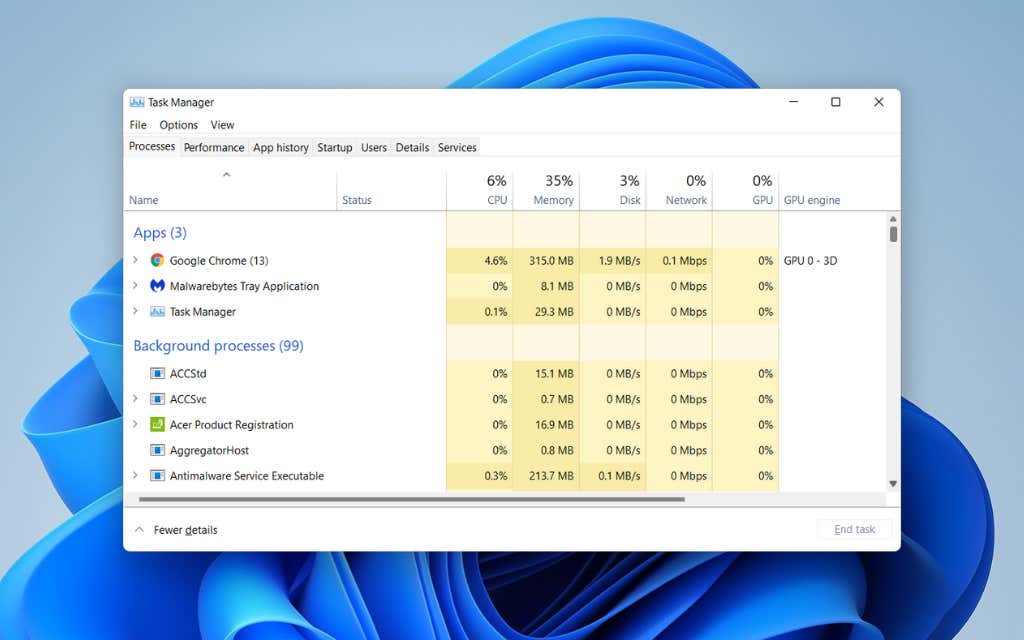
2. Windows Update Issues
Having a system that doesn’t want to update properly can be a pretty vexing scenario, especially when it’s causing a disruption to your workflow. Some common problems include updates failing to install, getting stuck during the install process or causing errors after the installation. Generally these issues can occur from various causes such as corrupt system files, insufficient disk space, miss-configured settings, or even conflicts with third-party software.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Check Update History: In your settings, go to Update & Security and then Windows Update and inspect the update history for failed installations.
- Run Windows Update Troubleshooter: Use the built-in troubleshooter found in your Update & Security section in your Settings tab to diagnose and resolve update issues.
- Ensure Sufficient Disk Space: Windows updates require free space for downloading and installing updates. Clear unnecessary files if needed.
- Verify Internet Connection: A stable connection is essential for downloading updates. Use a wired connection if Wi-Fi is unreliable.
- Run System File Checker: Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the command “sfc /scannow” to repair any corrupted system files.
Microsoft Resources:
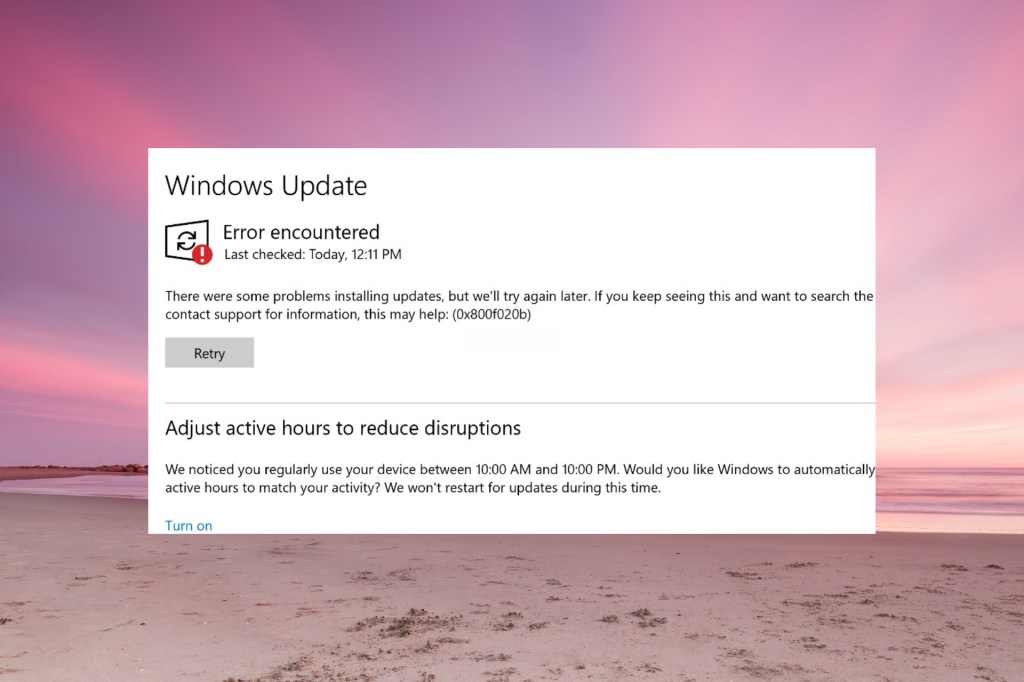
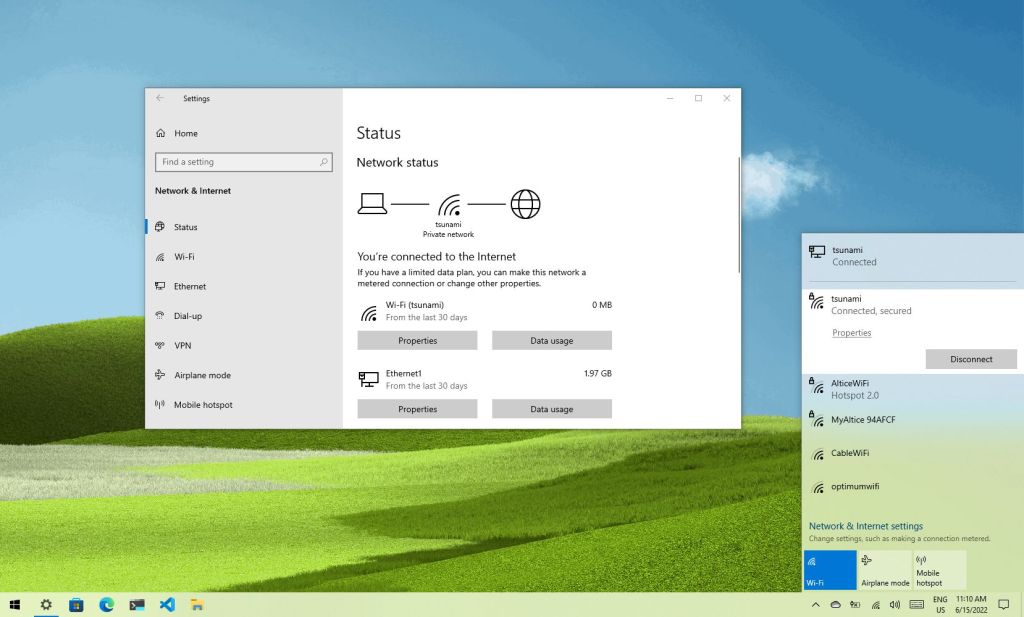
3. Wi-Fi Connectivity Problems
Wi-Fi connectivity issues can be a frustrating scenario, whether it’s a slow connection, frequent disconnections, or being unable to connect to the network altogether. These problems can arise from several different avenues such as router issues, outdated network drivers, incorrect network settings, or even interference from other devices.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Restart Router and Computer: Power cycling the router and PC often resolves temporary glitches.
- Verify Network Settings: Ensure the correct network is selected, credentials are accurate, and the network type (private or public) is correctly configured.
- Update Network Drivers: Outdated or corrupted drivers can prevent proper connectivity. Use Device Manager to update the drivers.
- Run Network Troubleshooter: Use the built-in troubleshooter found within the Settings tab.
- Check for Interference: Devices like microwaves or other wireless networks can cause interference. Try changing the router’s Wi-Fi channel.
Microsoft Resources:
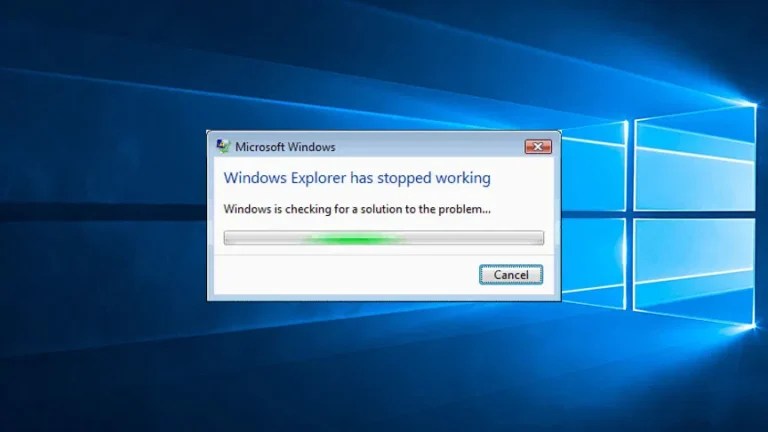
4. Windows Explorer Not Responding
When your windows explorer isn’t responding, it can be an annoyance, especially when you’re trying to access files. This issue can be occur when your system has insufficient system resources, malware, system errors, or even something like an outdated video driver can affect your file explorer.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Restart Windows Explorer: Open Task Manager, find Windows Explorer, right-click it, and select Restart.
- Run System File Checker: Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the command “sfc /scannow” to repair any corrupted system files that may be causing the issue.
- Update Graphics Drivers: Use Device Manager to check for updates to your display adapter.
- Scan for Malware: Run a full system scan using a reputable anti-malware tool.
- Boot into Safe Mode: If the problem persists, boot into Safe Mode. If the issue does not occur in Safe Mode, a startup program may be the culprit.
Microsoft Resources:
5. Computer Booting Slowly
It can be a very frustrating situation when you’re trying to boot up your system and it takes an eternity to load but fortunately it’s quite often a pretty easy fix. A windows machine can be boot slowly for any number of reasons, such as too many programs are set to launch at startup, you’re infected with malware, your hard-drive is running out of space, or potentially your CPU is a bit old and struggling.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Manage Startup Programs: Open Task Manager, go to the Startup tab, and disable any unnecessary programs.
- Free Up Disk Space: Ensure the boot drive has sufficient free space. Use Disk Cleanup to remove temporary files and system cache.
- Scan for Malware: Malware can consume resources and slow down the boot process. Run a full scan using a trusted antivirus.
- Check BIOS Settings: Access your BIOS/UEFI settings and enable features like Fast Boot if available.
- Upgrade to SSD: If the system uses a traditional HDD, consider upgrading to an SSD for significantly faster boot times.
Microsoft Resources:

Understanding common Windows issues and their resolutions can greatly improve system reliability and performance. By following these technical troubleshooting steps, you can save time, reduce frustration, and maintain an efficient computing environment. Regular system maintenance, such as keeping software updated and ensuring adequate hardware resources, is crucial for a smooth user experience.
Additional Resources:

Leave a comment