Depending on where you work, you may often hear the command line referenced as the “Network Command Line” when dealing with network related commands, this is because the network command line is a tool that utilizes the command line(or command prompt) to troubleshoot and configure network settings, but in this post we’ll be referring to it as the CLI (Command Line Interface).
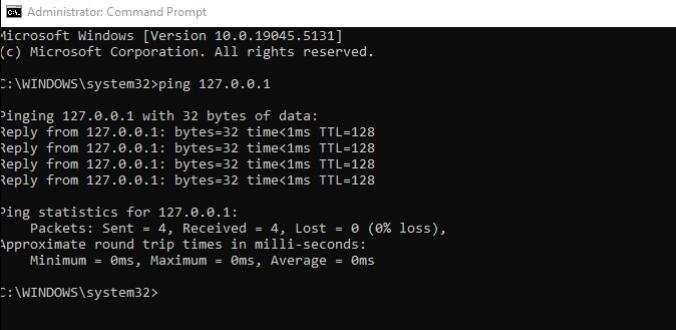
To access the Network Command Line, you’d just need to simply open your command prompt(CMD) or command line interface(CLI) and run your desired commands such as “ipconfig” or “ping 127.0.0.1”, but be advised that some commands may require elevated privileges, for example, “netstat -b”.
The Basics
There’s a multitude of windows commands you can use in the CLI for networking but you’ll likely not see or use a majority of them depending on your role but let’s get into the nitty gritty of the commands you’ll likely see!
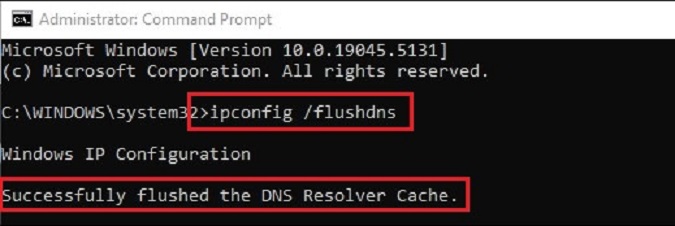
“ipconfig” – The ipconfig (Internet Protocol Configuration) command displays and manages network configuration info including, IP addresses, subnet masks, and gateways, basically it provides all the detailed information related to your computers network settings.
You can also use it for troubleshooting things such as connectivity problems, incorrect IP addressing, or clearing your DNS client resolver cache, which can assist with DNS-related connectivity problems.
“ping” – The ping command is probably the most used, if not most common command in this list and it’s used with IP addresses, for example, “ping 192.168.25.100”. It’s a command that tests if a device is reachable on a network but can also be used to test internet connectivity by pinging a public IP, such as Google’s DNS IP 8.8.8.8. If your ping test isn’t successful and you receive lines of text that say “Reply from xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx: Destination host unreachable.”, you could be experiencing an issue related to any number of things such as poor cabling, issues with the routing table, an incorrect IP address, or potentially even a firewall.

“arp” – The arp command is used to display and modify ARP tables that translate IP addresses to MAC addresses. These ARP tables are a pretty important component because without them we’d not be able to send IPv4 packets to other devices, as we need both their physical and logical address to send these packets. The most common arp commands that I use are typically “arp -a” which displays the arp cache of the computer I’m connect to and “arp -d [ip address]” which deletes the specified IP from the arp table.

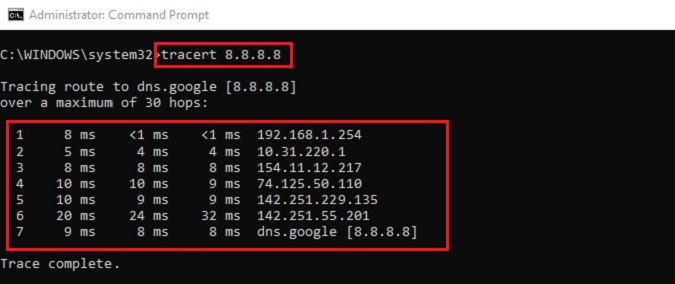
“tracert” – The tracert command provides a map of how data on the internet travels from it’s source to it’s destination. It’s generally used to diagnose network issues by tracking the IP address of routers and the time it takes for data to pass through each hop. This can be extremely useful for troubleshooting large networks where several paths can lead to the same point, as it’ll enable you to locate where the data was unable to be sent through, commonly known as a point of failure.
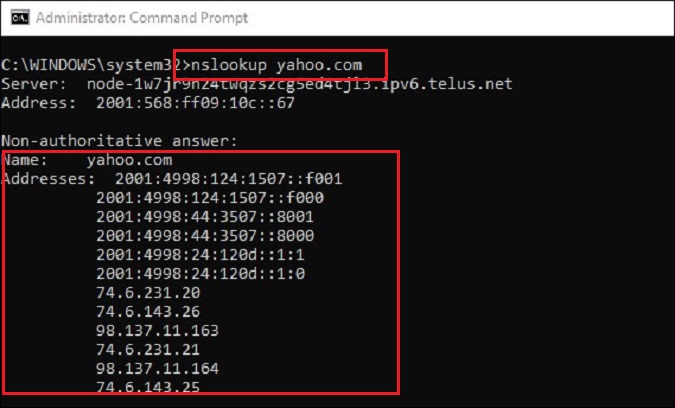
“nslookup” – The nslookup command is another helpful command used for troubleshooting DNS problems. It allows you to enter a host name/domain name and find out the corresponding IP. It can be used to find DNS records as well! As an example, if you’re not receiving emails to your domain and suspect your MX records have errors, you can cross-check with nslookup
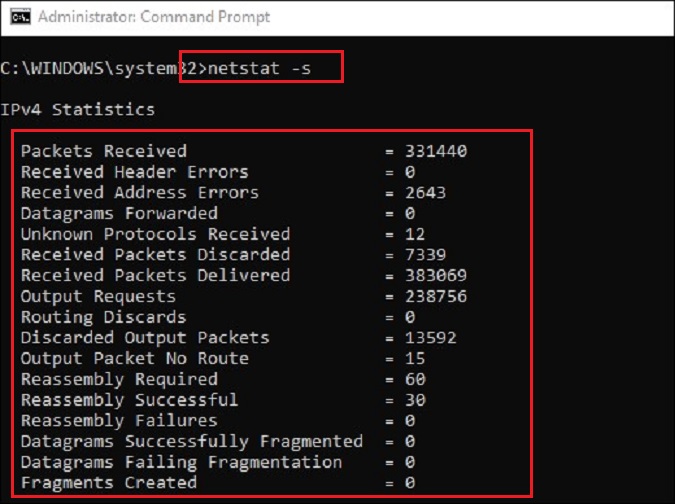
“netstat” – The netstat command is a networking tool primarily used for troubleshooting, configuration, and monitoring of network connections. It can display a variety of information such as the status of TCP/UDP endpoints, routing table information, what ports are listening, and can even be used to determine usage statistics.
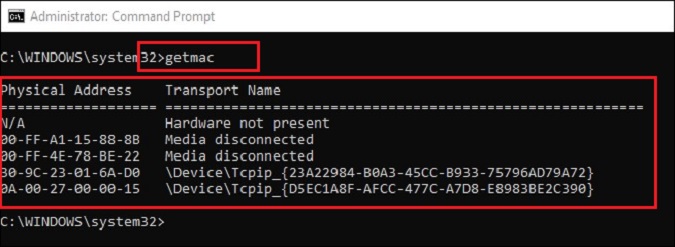
“getmac” – The getmac command is a command that is used to display the Media Access Control (MAC) addresses for each network adapter in a computer. The MAC address is the physical address associated with that adapter and is integral for network communications. Being able to find the MAC can be very important in troubleshooting situations.
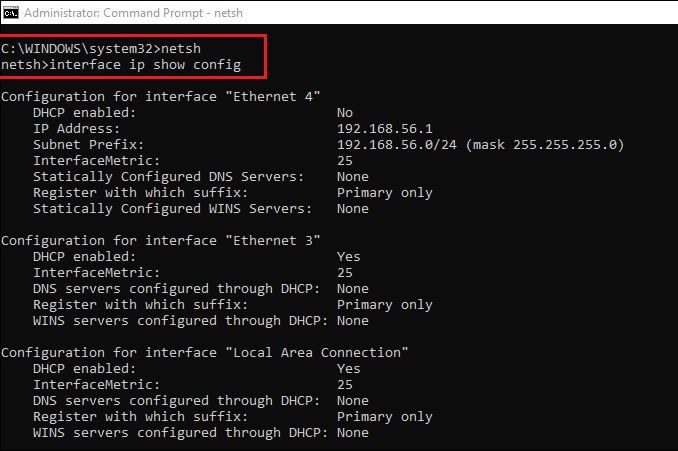
“netsh” – the netsh command is a command to open the Network Shell utility on windows and it included in all versions of windows since 2000. It’s a versatile tool that allows users to configure and display network communication status, diagnose and fix network issues, and perform network admin tasks such as automation or configuring IPs. Netsh can be used to perform many of the same functions as the control panel or Microsoft Management Console (MMC), but it also provides additional functionality. For example, it can manage network bridges, IPv6 objects and remote procedure calls.

Leave a comment